4.5 KiB
yale-access
Yale Access is a solution to allow passcodes to be added and removed to a Yale Smart Lock.
The solution is designed to be self-hosted, as it will need access to a ZWave.JS server to communicate with the lock.
Prerequisites
A few pre-requisites are required for this application:
- A Yale Smart Lock (I have an Assure Lock SL)
- A ZWave.JS server
Installation
Yale Access is best run as a Docker container, as this reduces almost all hosting compexity. The application will need to be hosted on the internal network on your home (though the application can be exposed to the internet if you wish).
Preparing the lock
The lock will need to be paired with a ZWave.JS server, I suggest using . Once the lock is paired you will need to set a value for all the user codes you wish to use (this prevents null values being returned from the lock). To do this navigate to the lock in the ZWave.JS UI, and click the 'User Code v1' option. For each user code you are intending to use set the status to 'Available'.
Docker
A sample docker compose file is provided in the repository. This can be used to get up and running quickly.
The appropriate environment variables will need to be set in the docker compose file. These are:
Frontend
- NUXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_URL - The URL of the backend API
Backend
- LogLocation - The location to store logs, this path should also be mounted as a local volume, to ensure logs are not lost when the container is restarted.
- CorsAllowedOrigins - A comma separated list of allowed origins for CORS requests. This should be set to the URL of the frontend.
- Devices__YaleLockNodeId - The Node ID of the Yale Lock as found in the ZWave.JS interface.
- Codes__Home - The code ID to use as the 'home' code. This will have extra UI functionality, to prevent it from being updated or deleted accidentally.
- Codes__GuestCodeRangeStart - The start of the range of codes to use for guest codes. This should be set to the first code that is available for use.
- Codes__GuestCodeRangeCount - The number of codes to use for guest codes. This should be set to the number of codes that are available for use.
- ZWave_Url - The URL of the ZWave.JS server.
- ZWave_SchemeVersion - The scheme version of the ZWave.JS server. This should be set to the scheme version of the ZWave.JS server.
- Authentication_Password - The password to use for authentication. This should be set to a strong password.
- Twilio__AccountSid - The Account SID for the Twilio account to use for sending SMS messages.
- Twilio__AuthToken - The Auth Token for the Twilio account to use for sending SMS messages.
- Twilio__FromNumber - The number to send SMS messages from.
Once the environment variables have been set, the application can be started by running docker-compose up -d from the root of the compose file. To allow the application to be accessed from the internet, you will need to expose the application to the internet, the recommended setup would be a Nginx reverse proxy.
Screenshots
Login
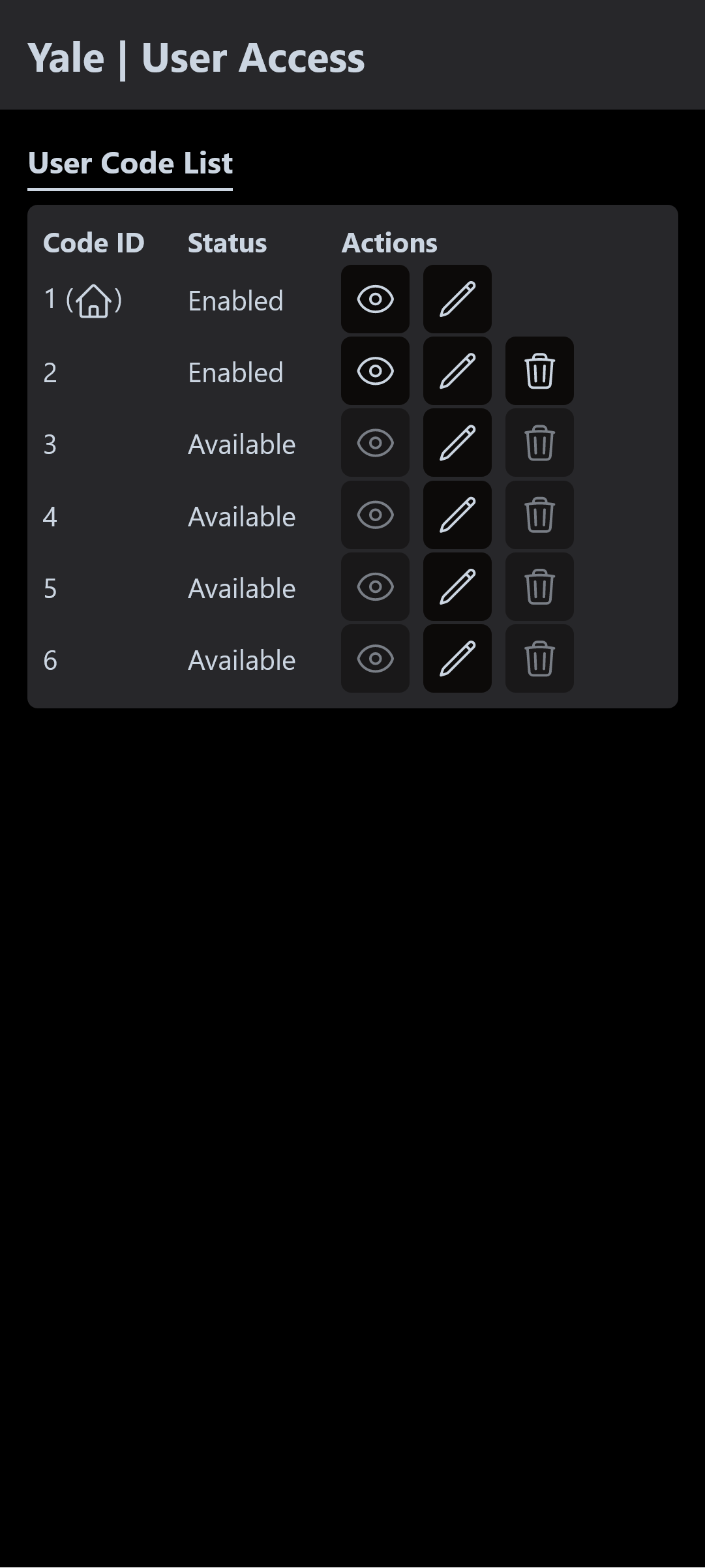
Home Screen
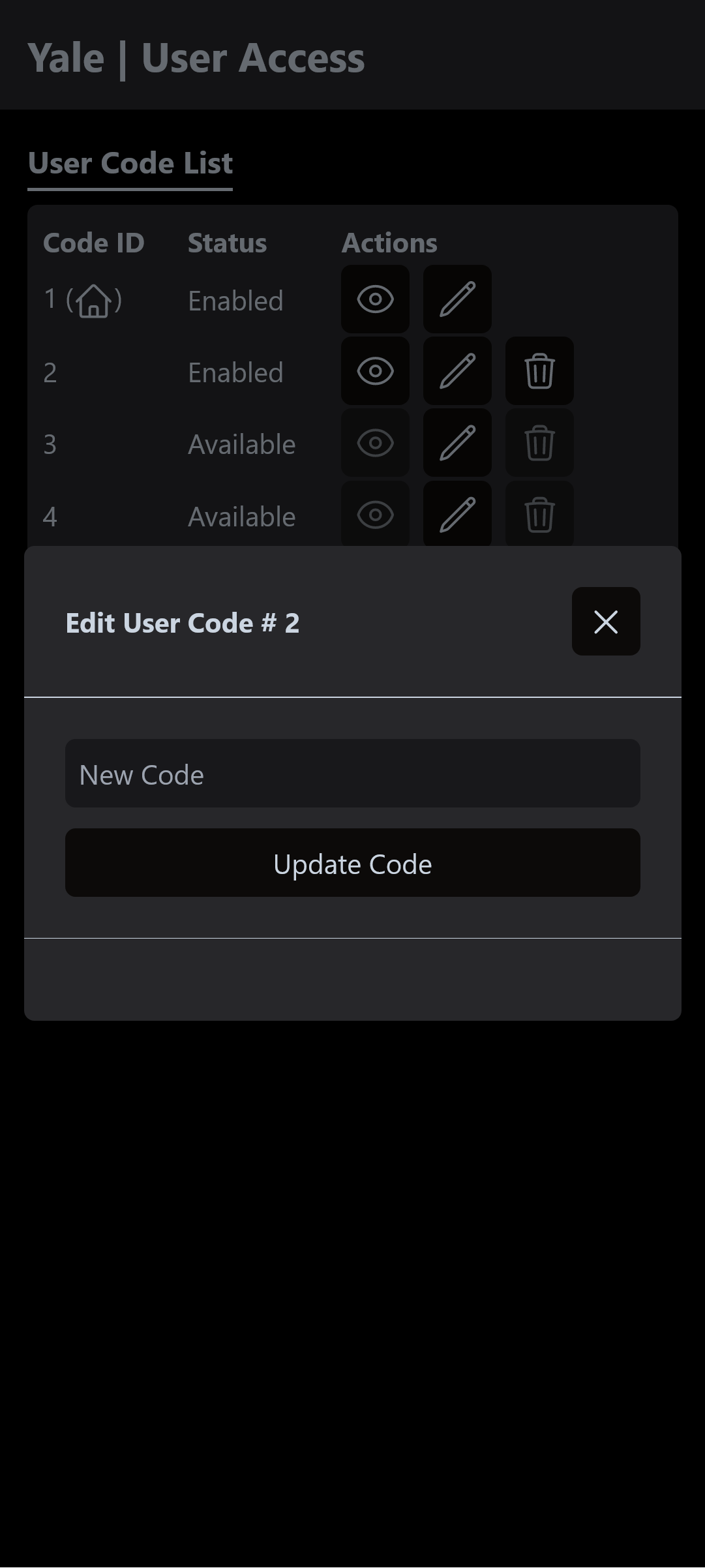
Edit Code
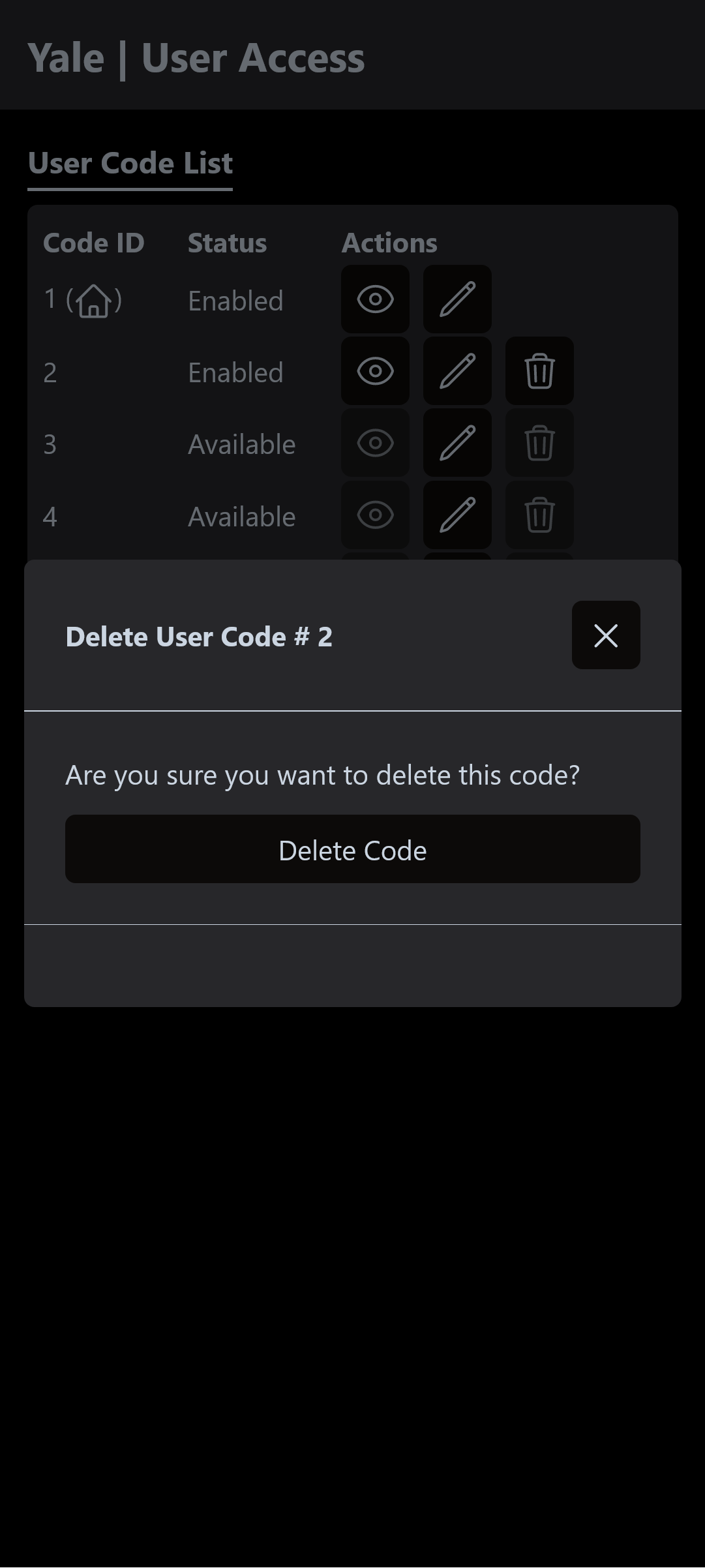
Delete Code
Development
Frontend
The frontend is built using Nuxt. To get started ensure you have node install (latest LTS is recommended), and run yarn install to install all dependencies.
To start the development server, run yarn dev.
Backend
The backend is built using .NET 7. To get started ensure you have the .NET 7 SDK installed. Open the solution in Visual Studio and ensure that the appropriate user secrets are set. A secrets.template.json file is provided in the repository. This should be copied to secrets.json and populated with the appropriate values.
To start the backend, run dotnet run from the YaleAccess.Api directory (or use the Visual Studio debugger).
Note: you will need the ZWave.JS server running and configured to use the same scheme version as the backend for development unsless you are using the mock mode.
To enable the mock mode for development, set the UseMockDevelopmentMode flag to true in the appsettings.Development.json file. This will repalce teh ZWave.JS server with a mock implementation, which will allow you to test the application without a ZWave.JS server. This is handy for doing UI changes without having to have the lock available.